






 |
 |

SRML Glossary — "A"

Special thanks to NREL

We'd like to thank the National Renewable Energy Laboratory for
making available to us their glossary, which is the basis of ours. We've
edited and reformatted it, and linked it to our Web pages, and we'll continue
to add our own specialized terms, illustrations, and examples. Please note that
the Solar Radiation Monitoring Laboratory takes full responsibility for any
inaccuracies that may occur.

Links to other glossary sections:

A B C
D E F G
H I J K
L M N O
P Q R S
T U V W
X Y Z


|
|
|
|
An instrument
used for very accurate measurements of solar irradiance.
Absolute cavity radiometers absorb radiation on a blackened conical receiver
and are electrically self-calibrating. Absolute cavity radiometers determine
the solar constant and provide the reference
from which other radiometers are calibrated.
Here is a picture of an absolute
cavity radiometer used to transfer the
World Radiometric Reference (WRR) to all radiometers
calibrated at the Solar
Radiation Research Laboratory.
|
| |
The mass (in grams) of water in a volume (cubic meter) of air; units are g/m3.
|
| |
When the substance of interest is captured by another substance, reducing the amount
available. For examble, solar energy is absorbed by some atmospheric molecules, solar
collectors, and the ocean.
|
| |
Excluding weather and clouds, any small particle that tends to stay in the air, such as
smoke, dust, salt, and pollen.
|
| |
(Technically
known as the relative aerosol optical depth) Usually considered to
be synonymous with the airmass, is the approximate
number of aerosols in a path through the atmosphere relative to the standard
number of aerosols in a vertical path through a clean, dry atmosphere at
sea level.
|
| |
Atmospheric Environment Service,
the Canadian equivalent of USA's
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
AES operates the solar measurement network for Canada.
They are also the equivalent of USA's
National Climatic Data Center
in that they respond to requests for weather data and maintain the data archives.
|
| |
Automatic
Hickey-Frieden absolute cavity
radiometer. This is the model designation given by The Eppley Laboratory,
Inc. for their commercial version of an electrically self-calibrating absolute
cavity radiometer used to define and transfer the World Radiometric Reference
(WRR) to pyrheliometers and pyranometers used for
solar irradiance measurements. The WRR is maintained at the World
Radiation Center, Davos, Switzerland for the World
Meteorological Organization.
|
| |
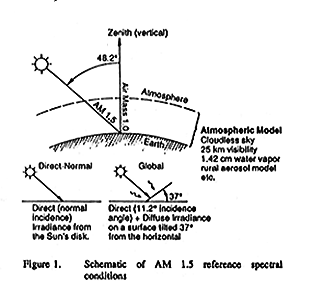
The relative
path length of the direct solar beam radiance through the atmosphere. When
the sun is directly above a sea-level location the path length is defined
as airmass 1 (AM 1.0). AM 1.0 is not synonymous with solar noon because
the sun is usually not directly overhead at solar noon in most seasons and
locations. When the angle of the sun from zenith
(directly
overhead) increases, the airmass increases approximately by the secant of
the zenith angle. A better calculation (Kasten, F. and A. T. Young
(1989). Revised optical air mass tables and approximation formula. Applied
Optics 28 (22), 4735-4738) follows:
m = 1.0 / [ cos(Z) + 0.50572 * (96.07995
- Z)-1.6364]
where Z is the solar zenith angle.
The figure below illustrates the concept of airmass.
|
| |
The fraction of solar radiation that is reflected. The solar energy community defines
albedo as the fraction of solar radiation that is reflected from the ground, ground cover,
and bodies of water on the surface of the earth. Astronomers and meteorologists include
reflectance by clouds and air. To reduce confusion, some solar researchers use the term
ground reflectance.
|
| |
The set of simple instructions that combine to accomplish a task. Computer codes are
algorithms.
|
| |
Air temperature
measured with a thermometer, similar to dry-bulb
temperature.
|
| |
An instrument that measures wind speed.
|
| |
The angle
that a ray (of solar energy, for example) makes with a line perpendicular
to the surface. For example, a surface that directly faces the sun has a
solar angle of incidence of zero, but if the surface is parallel to the
sun (for example, sunrise striking a horizontal rooftop), the angle of incidence
is 90°. The figure accompanying the description of airmass
illustrates a solar angle of incidence of 48.2° to a horizontal surface.
|
| |
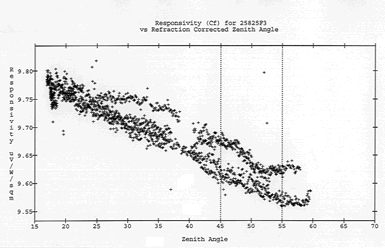
Quantifying
the effects of radiance incidence angle on pyranometer
measurement performance. If a pyranometer is rotated while a beam of light
is shined upon it, it will record the maximum energy when it is directly
facing the beam, and the energy will fall to zero when it is sideways to
(or facing away from) the beam. A graph of the energy reported by the pyranometer
as the angle it makes with the beam of light should look like the cosine
of the angle, if the instrument were perfect. Pyranometers have imperfections
that keep them from producing this curve. The determination of the true
behavior of the pyranometer as the angle it makes with the light beam changes
is called angular response characterization (see graph below for an example).
|
| |
The
American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers.
|
| |
The zone of air that surrounds a planet.
|
| |
The pressure (force per area) created by the weight of the atmosphere. At
higher elevations, the atmospheric pressure is lower because there is less air.
|
| |
Haziness in the atmosphere due to
aerosols such as dust (particles ranging from 0.1 to 1+ microns in diameter).
If turbidity is zero, the sky has no dust. A sun photometer is used to
measure atmospheric turbidity.
|
| |
Loss of a
substance as it is deflected, fragmented, or absorbed. For example, solar
irradiance attenuates as it passes through
the atmosphere to the surface of the earth.
|
| |
The angle between the
horizontal direction (of the sun, for example) and a reference direction (usually North,
although some solar scientists measure the solar azimuth angle from due South).
|
| |
|

Links to other glossary sections:

A B C
D E F G
H I J K
L M N O
P Q R S
T U V W
X Y Z



© 2022, UO Solar Radiation Monitoring
Laboratory.
 Last
revised: March 4, 2022. Last
revised: March 4, 2022.


Home
page URL: solardata.uoregon.edu |


