






 |
 |

SRML Glossary — "S"

Special thanks to NREL

We'd like to thank the National Renewable Energy Laboratory for
making available to us their glossary, which is the basis of ours. We've
edited and reformatted it, and linked it to our Web pages, and we'll continue
to add our own specialized terms, illustrations, and examples. Please note that
the Solar Radiation Monitoring Laboratory takes full responsibility for any
inaccuracies that may occur.

Links to other glossary sections:

A B
C D E F
G H I J
K L M N
O P Q R
S T U V W
X Y Z


|
| |
Air that has the maximum amount of water vapor; any increase in water vapor will cause
condensation.
|
| |
Radiation
that has been reflected from particles, disrupting the original direction
of the beam.
 Click Shining On
(Figure 3) to see solar components Click Shining On
(Figure 3) to see solar components
|
| |
A material
that has much lower resistance to the flow of electrical current in one
direction than in another. Diodes, transistors, and many photovoltaic
cells contain semiconductive materials.
|
| |
The Solar Energy Research Institute, which became the
National Renewable Energy Laboratory in 1991.
|
| |
A disk on
a tracking arm which blocks the direct
normal irradiance so as to allow a pyranometer
to measure only the diffuse sky radiation.
Below is a picture of a pyranometer shaded by a shading disk.

|
| |
A metal
strip which blocks the direct normal
radiation so as to allow a pyranometer
to measure only the diffuse sky radiation.
Below is a picture of a pyranometer shaded by a shadow band.

|
| |
The principal
portion of the solar spectrum that spans
from approximately 300 nanometers (nm) to 4000 nm in the electromagnetic
spectrum. Longwave radiation
is infrared radiation (>4000 nm).
|
| |
A photovoltaic
cell that is being used to measure solar
irradiance. Because its spectral response is not as exact as that of
thermopile instruments, it has a higher
uncertainty.
|
| |
Refers to the appearance of the entire sky, from horizon to zenith in all directions.
Below is a picture of the sky dome at the
Solar Radiation Research Laboratory taken by an all-sky camera.

|
| |
Synonymous
with diffuse sky radiation, the
radiation component that strikes a point from the sky, excluding circumsolar
radiation. In the absence of atmosphere, there should be almost no sky
radiation. High values are produced by an unclear atmosphere or reflections
from clouds.
 Click Shining On
(Figure 3) to see solar components Click Shining On
(Figure 3) to see solar components
|
| |
A photovoltaic
cell that is used to convert solar energy into electricity.
|
| |
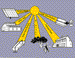
A device that receives solar energy and converts it to useful energy forms. The following
figure from
Shining On illustrates several types of solar collectors.
|
| |
A solar
collector that enhances solar energy by focusing it onto a smaller area
through mirrored surfaces or lenses.
|
| |
Although
not strictly constant, this number is the amount of solar power flux
that passes through the mean Earth orbit. The currently accepted value is
1367 W/m2. Note that Earth-based instruments record lower values
of solar power flux because of atmospheric attenuation.
|
| |
Collective name for all methods for converting
the sun's energy into usable energy.
|
| |
Technology for using concentrated sunlight to break down
and destroy hazardous waste.
|
| |
Technology for converting sunlight directly into electricity.
|
| |
Method for harnessing, storing, and using the sun's energy.
|
| |
Methods for converting biomass into fuels and by-products.
|
| |
Technology to harness the sun's energy for heating buildings, air, and water for
industrial and household uses.
|
| |
The amount
of solar energy that arrives at a specific area of a surface during a specific
time interval (radiant flux density). A typical
unit is W/m2.
|
| |
The time
at which the position of the sun is at its highest elevation in the sky.
At this time, the Sun is either due South (typically in the Northern Hemisphere)
or due North (typically in the Southern Hemisphere). This time can be quite
different from noon according to local
standard time.
|
| |
The electromagnetic
radiation emitted by the sun.
|
| |
The electromagnetic
spectral distribution emitted by the sun or received by a collector
or instrument on Earth. For example, Figure 2 from Shining
On below shows the solar spectrum as measured in space and on the Earth's
surface.

|
| |
Technology for using the sun's energy to produce steam to run turbines that generate electricity.
|
| |
The 26 measurement
sites in the 1952-1975 SOLMET/ERSATZ solar &
meteorological hourly network that measured global
horizontal solar radiation. The SOLMET/ERSATZ network has been replaced
by the 1961-1990 National
Solar Radiation Data Base.
|
| |
Pertaining to space, or pertaining to distance such as spatial variation
(variation over distance).
|
| |
The solar
spectral distribution.
|
| |
The amount
of radiant energy flux expressed in terms of the
solar spectrum. NREL's
Solar Spectral Radiation Data Base contains thousands of irradiance
spectra.
|
| |
An instrument
designed to measure spectral irradiance.
Spectroradiometers gathered the data in NREL's
Solar Spectral Radiation Data Base.
|
| |
The Solar Radiation Research Laboratory at
the National Renewable Energy Laboratory.
|
| |
The relatively isothermal (constant temperature) layer of the atmosphere above the troposphere
and below the mesosphere.
|
| |
Used interchangeably
with the more precise term bright sunshine,
when the sun casts an obvious shadow or when a Campbell-Stokes
sunshine recorder is recording, usually above 210 W/m2.
|
| |
The length
of time for which the sun casts an obvious shadow or when a Campbell-Stokes
sunshine recorder is recording. The lower limit for bright sunshine
(based on a Campbell-Stokes recorder) is between 70 W/m2 (very
dry air) and 280 W/m2 (very humid air).
|
| |
The location
of the sun in the sky, expressed in terms of azimuth
angle and zenith angle.
|
| |
A unit which
multiplies the amount of energy the Earth can receive from the sun, typically
used by the solar concentrator community;
e.g., a concentrator might focus the energy of 40 suns onto a central
receiver. Note that this unit is not precisely defined, and is usually
less than the solar constant.
|
| |
|

Links to other glossary sections:

A B
C D E F
G H I J
K L M N
O P Q R
S T U V W
X Y Z



© 2022, UO Solar Radiation Monitoring
Laboratory.
 Last
revised: April 5, 2022. Last
revised: April 5, 2022.


Home page URL: solardata.uoregon.edu |
 Click Shining On
(Figure 3) to see solar components
Click Shining On
(Figure 3) to see solar components
 Click Shining On
(Figure 3) to see solar components
Click Shining On
(Figure 3) to see solar components





