






 |
 |

SRML Glossary — "L"

Special thanks to NREL

We'd like to thank the National Renewable Energy Laboratory for
making available to us their glossary, which is the basis of ours. We've
edited and reformatted it, and linked it to our Web pages, and we'll continue
to add our own specialized terms, illustrations, and examples. Please note that
the Solar Radiation Monitoring Laboratory takes full responsibility for any
inaccuracies that may occur.

Links to other glossary sections:

A B
C D E F
G H I J
K L M N O
P Q R S
T U V W
X Y Z


|
| |
Named for
Samuel P. Langley (1834-1906), a pioneering solar energy researcher at the
Smithsonian Institution, this unit of radiant flux
is one calorie per square centimeter (cal/cm2).
|
| |
The angular distance from the equator to the pole. The equator is 0°, the North Pole
is 90° North, and the South Pole is 90° South.
|
| |
Usually
the visual portion of the electromagnetic
spectrum between infrared (about 8000 Angstroms or 800 nanometers(nm))
and ultraviolet (about 4,000 Angstroms or 400 nm); however, the term is
sometimes used as a synonym for all electromagnetic radiation.
|
| |
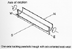
A system that tracks the path of the sun by pivoting on one axis (typically East-West or
North-South), using shiny parabolic troughs to heat the collector fluid that passes through
a tube at the focus. It derives its name from the fact that solar radiation is focused
on a line instead of on a point. The cover of the publication Solar Radiation Data Manual for Flat-Plate
and Concentrating Collectors has an illustration of concentrating collectors.
|
| |
The time
of day based strictly on the longitude of
the locality and not on "blocky" time zones. For example, when it is 12:00
Pacific Standard Time (USA) (assumed to be 120° West Longitude), it
is 11:51 Local Apparent Time in Seattle, Washington (USA), at 122° 18'
West Longitude.
|
| |
The time
of day based on the longitude of the zone
meridian associated with a locality. In the USA, the zone meridians
are known by the following names:
LONGITUDE NAME
75° West Eastern Standard Time
90° West Central Standard Time
105° West Mountain Standard Time
120° West Western Standard Time
135° West Alaska Standard Time
150° West Hawaii Standard Time
|
| |
The East-West angular distance of a locality from the Prime Meridian. The
Prime Meridian is the location of the Greenwich Observatory in England and all points
North and South of it.
|
| |
Infrared
radiation, radiation with wavelengths greater than those of the visible
light (at about 8000 Angstroms or 800 nanometers(nm)) but shorter than those
of microwaves (at about 1,000,000 Angstroms or 800,000 nm). Longwave radiation
is associated with heat energy.
|
| |
The International Standard (SI) unit of measure for luminous flux density
at a surface. One Lux equals one lumen per square meter.
|
| |
|

Links to other glossary sections:

A B
C D E F
G H I J
K L M N O
P Q R S
T U V W
X Y Z



© 2022, UO Solar Radiation Monitoring
Laboratory.
 Last
revised: April 1, 2022. Last
revised: April 1, 2022.


Home page URL: solardata.uoregon.edu |

